
 |
Case Study: RS-485 Robust Industrial Control Communications System |
Introduction
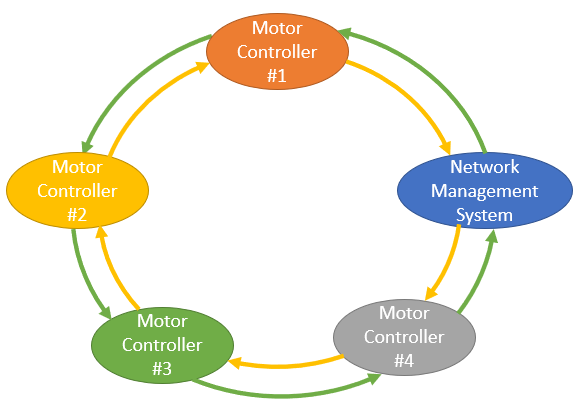
RS-485 Overview RS-485 is a low cost, standardized solution for industrial Local Area Network(LAN) communcations. RS-485 supports full duplex operation upto 10 Mbit/s, over short distances. The signaling technology allows for a trade-off between bit rate and distance. Distances of several hundred meters can be traversed in a single hop but at a correspondingly lower data rate. |

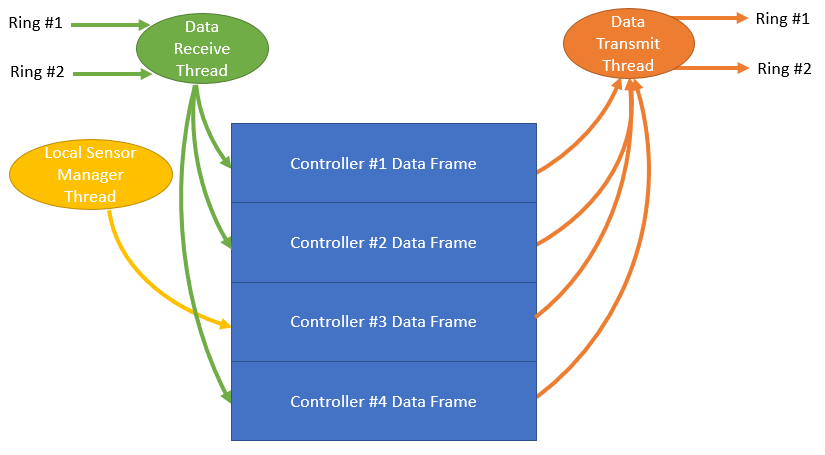

Summary
The longest data run in the network was 210 meters and the network was able to run at 1M bps over CAT-5 cable.Copyright© 2024 Delta Numerix.
Permission is granted to create WWW pointers to this document. |